Click on the links below to find out more
KNEE ARTHRITIS
TREATMENT
There is no cure for arthritis but there are a number of treatments that may help relieve the pain and disability it can cause.
NONSURGICAL TREATMENT
As with other arthritic conditions, initial treatment of arthritis of the knee is nonsurgical. Your doctor may recommend a range of treatment options.
LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS
Some changes in your daily life can protect your knee joint and slow the progress of arthritis.
Minimize activities that aggravate the condition, such as climbing stairs.
Switching from high impact activities (like jogging or tennis) to lower impact activities (like swimming or cycling) will put less stress on your knee.
Losing weight can reduce stress on the knee joint, resulting in less pain and increased function.
PHYSIOTHERAPY
Specific exercises can help increase range of motion and flexibility, as well as help strengthen the muscles in your leg.
MEDICATIONS
Several types of drugs are useful in treating arthritis of the knee. Because people respond differently to medications, your doctor will work closely with you to determine the medications and dosages that are safe and effective for you.
Over-the-counter, non-narcotic pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications are usually the first choice of therapy for arthritis of the knee. Acetaminophen is a simple, over-the-counter pain reliever that can be effective in reducing arthritis pain.
ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES
Many alternative forms of therapy are unproven, but may be helpful to try, provided you find a qualified practitioner and keep your doctor informed of your decision.
Assistive devices
Using devices such as a cane, wearing shock-absorbing shoes or inserts, or wearing a brace or knee sleeve can be helpful. A brace assists with stability and function, and may be especially helpful if the arthritis is centered on one side of the knee. There are two types of braces that are often used for knee arthritis: An “unloader” brace shifts weight away from the affected portion of the knee, while a “support” brace helps support the entire knee load.
Other remedies. Applying heat or ice, using pain-relieving ointments or creams, or wearing elastic bandages to provide support to the knee may provide some relief from pain.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
As with all surgery, there are risks and possible complications. Dr Slattery will discuss the possible complications with you before your operation.
ARTHROSCOPY
During arthroscopy small incisions and thin instruments (keyhole surgery) are used to diagnose and treat joint problems. Arthroscopic surgery is not recommended to treat isolated arthritis of the knee. In cases where osteoarthritis is accompanied by a degenerative meniscal tear which is causing mechanical symptoms, arthroscopic surgery may be recommended to treat the torn meniscus.
CARTILAGE GRAFTING
Normal, healthy cartilage tissue may be taken from another part of the knee or from a tissue bank to fill a hole in the articular cartilage. This procedure is typically considered only for younger patients who have small areas of cartilage damage.
SYNOVECTOMY
If the joint lining (synovium) is inflamed and irritated, this can be removed to relieve pain and swelling.
Osteotomy
In a knee osteotomy, either the tibia (shinbone) or femur (thighbone) is cut and then reshaped to relieve pressure on the knee joint. Knee osteotomy is used when you have early-stage osteoarthritis that has damaged just one side of the knee joint. By shifting your weight off the damaged side of the joint, an osteotomy can relieve pain and significantly improve function in your arthritic knee.
TOTAL OR PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT (ARTHROPLASTY)
Dr Slattery will remove the damaged cartilage and bone, and then position new metal or plastic joint surfaces to restore the function of your knee.
For more information on Total or Partial Knee Replacement, click here
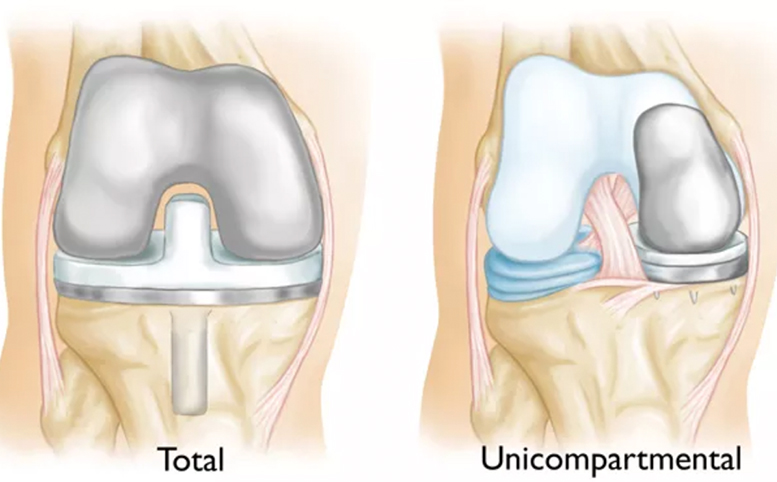
(Left) A partial knee replacement is an option when damage is limited to just one part of the knee. (Right) A total knee replacement prosthesis.
RECOVERY
After any type of surgery for arthritis of the knee, there is a period of recovery. Recovery time and rehabilitation depends on the type of surgery performed. In most cases, surgery relieves pain and makes it possible to perform daily activities more easily.